Blacktooth Laser Cutter Redux and Review
Executive summary
The Blacktooth Laser Cutter is a laudable experiment in producing a low-cost laser cutter and engraver from a time when commercial options were mostly over $15K USD, despite the cost of the component technologies having come way down. A significant amount of adjustment and modification is necessary to make the Blacktooth serviceable for any particular application. For those with a strong DIY ethos who enjoy tinkering with their equipment, it is likely still a solid option for a small shop or maker space. For most people looking for a laser to use as a general purpose shop or studio tool, there are now options requiring less tinkering and, with a shallower learning curve.
Update: I handed the Blacktooth laser off to a local school with a nascent maker space in 2019. In addition to a very competent teacher supervising the project, they have a literal rocket scientist available to assist.
Start

The Blacktooth laser started as a Kickstarter campaign in October of 2012 [1]. Behind it was a team that was already building other affordable CNC equipment, BuildYourCNC [2]. The Kickstarter campaign failed to get enough support but, they decided to proceed with the project and, generously, to honor the price offered to backers during the campaign.
So, in April of 2013, my factory-assembled Blacktooth Laser Cutter arrived, well-wrapped, on a large wooden palette. Getting it set up and in any way operational took me awhile.
Documentation and Support
The documentation for the Blacktooth is basically the assembly instructions [3] and, whatever you can glean from the support forums. Mine required an additional shipment of fasteners and, a few exchanges with support to understand what was part of the machine assembly and, what was for protection during shipping.
It is important to note that the DIY ethos runs very deep in the community of people using the Blacktooth. It quickly became clear from exchanges in the forums that no two users really have the same machine. Everyone has modified their Blacktooth significantly from the original design.Typical changes include homing limit switches, which make it easier to set the origin point and avoid driving the laser head beyond its actual range; upgraded air assist; filtration systems and digital signal processors (DSP).
BuildYourCNC was enthusiastic and quick to respond to my support inquiries. There were some initial issues where the employee helping me left the company, stopped responding and, no one took over monitoring their email address. They may need a support ticketing system. I noted that they were guarded or vague about some topics (like exhaust filtration and venting, safety equipment, etc.), presumably for liability reasons. Most of the responses I got from BuildYourCNC support were along the lines of a starting place to figure it out rather than a complete solution.
Software
Most commercial laser cutters have a component called a digital signal processor or DSP. The DSP is a sort of purpose-built computer that takes input in a standard format (typically raster and vector image formats) and, converts them into the signals that control the movement of the laser cutter. In most cases, this allows the operator to use standard image editing software and feed their jobs to the laser cutter as if it were a printer.
By contrast, the original stock Blacktooth Laser Cutter operates like a CNC machine. The movements of the laser are controlled by sending gcode (a standard CNC control language) instructions from CNC control software running on the operator’s computer. There are a number of options for this software but, one of the most common and, the one recommended for the Blacktooth is the Windows-based Mach3 [4].
There is also an opensource package that runs on Linux, predictably named LinuxCNC [5]. While I did not realize this was a workable option early on, I did later get it working with the Blacktooth. The UI is less polished but, it seemed serviceable.
Mach3 and LinuxCNC are just control software for sending gcode to the Blacktooth. To produce the the gcode for a particular design to send to the machine requires additional software. This is called computer-aided machining or CAM. I opted to work with a commercial CAM package called CamBam [6].
There are some idiosyncrasies with the Blacktooth (and any other CNC equipment, almost certainly) with regard to how specific gcode instructions are handled. Tweaking the settings in the CAM software to get the right gcode output for a particular machine can be a fiddly process. Variations in construction and the modifications people have made to their machines means that the same settings will not necessarily work the same way for anyone else.
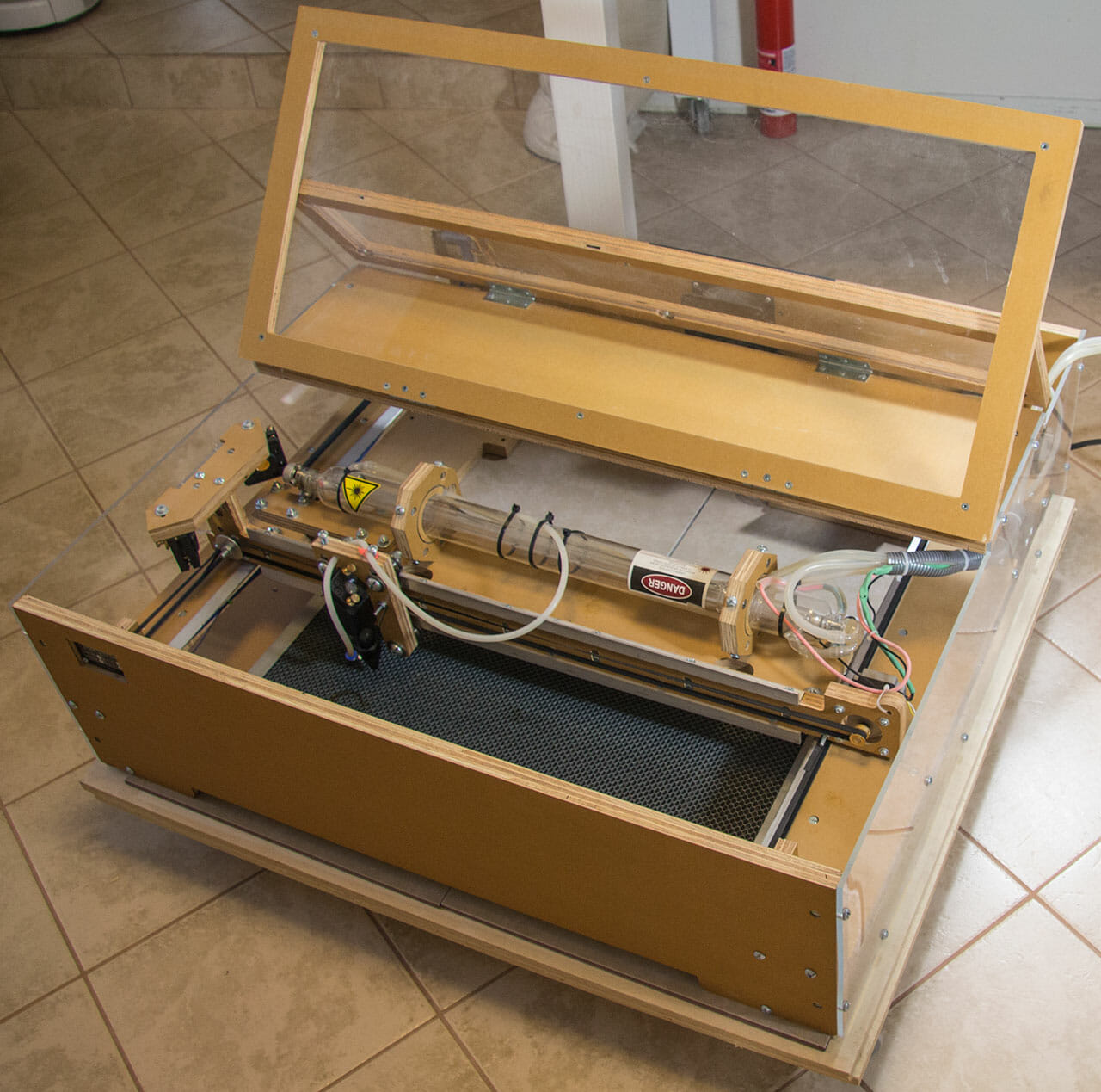
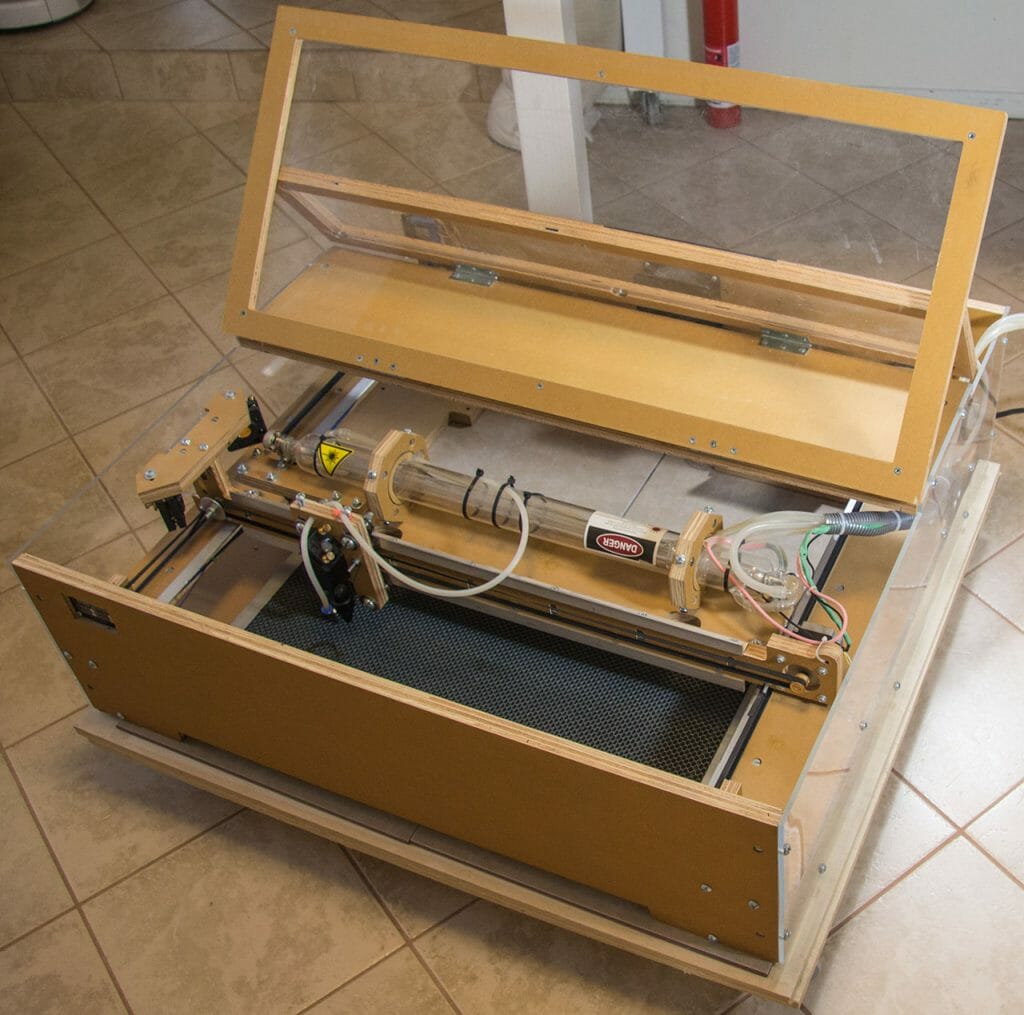
Hardware
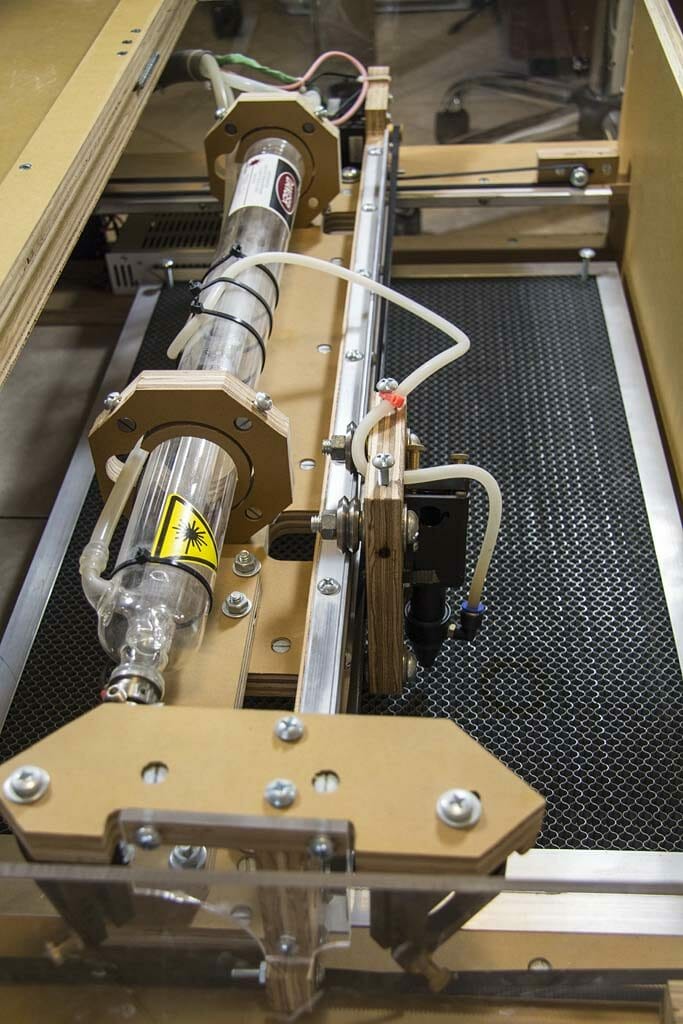
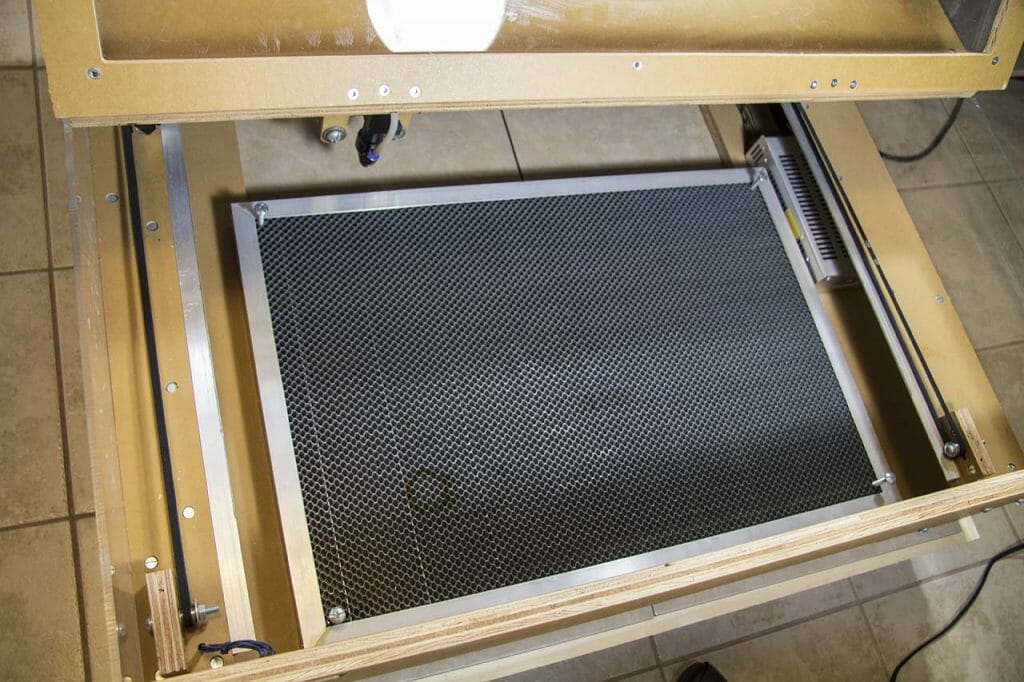
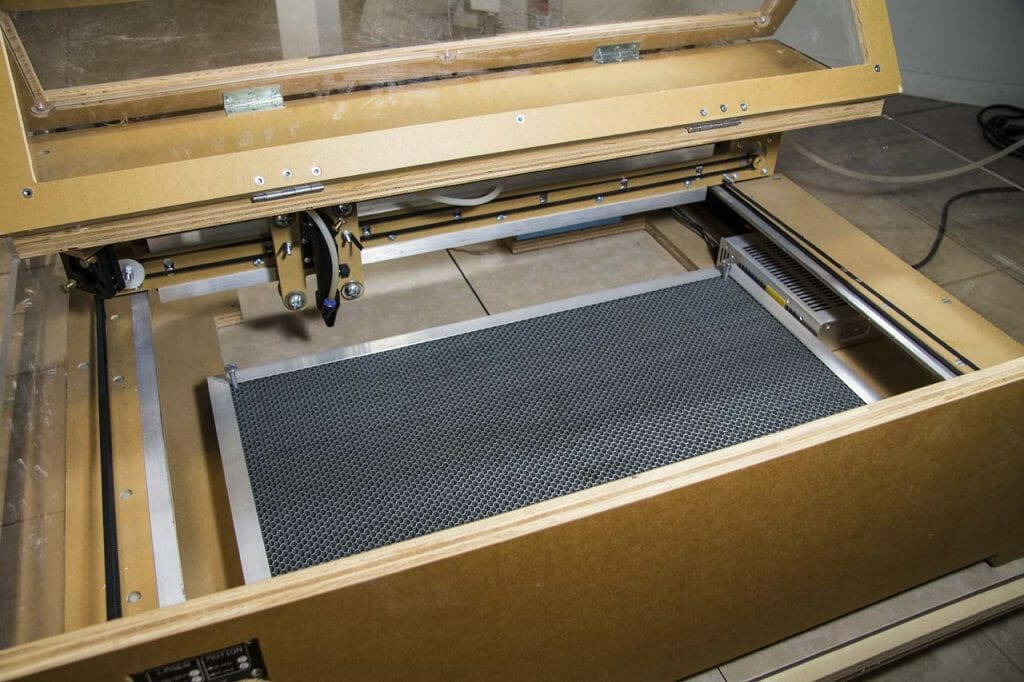
The Blacktooth has a generous 24” by 20” cutting bed. The bottom of the case is open to allow working on larger surfaces.

In the original stock model, power is controlled by a potentiometer on the side of the case.
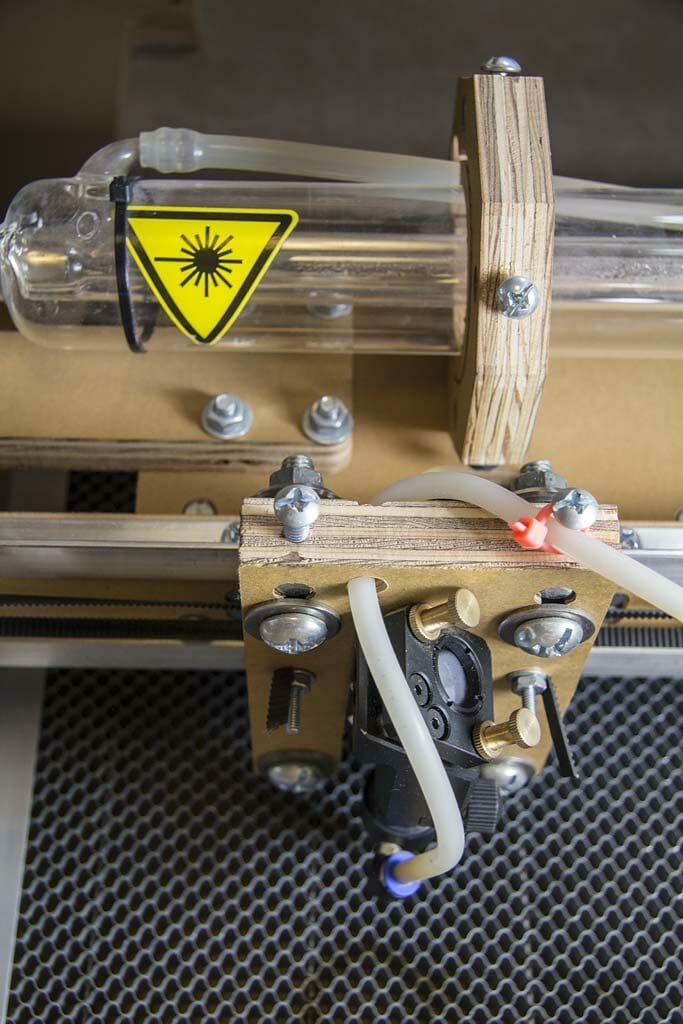
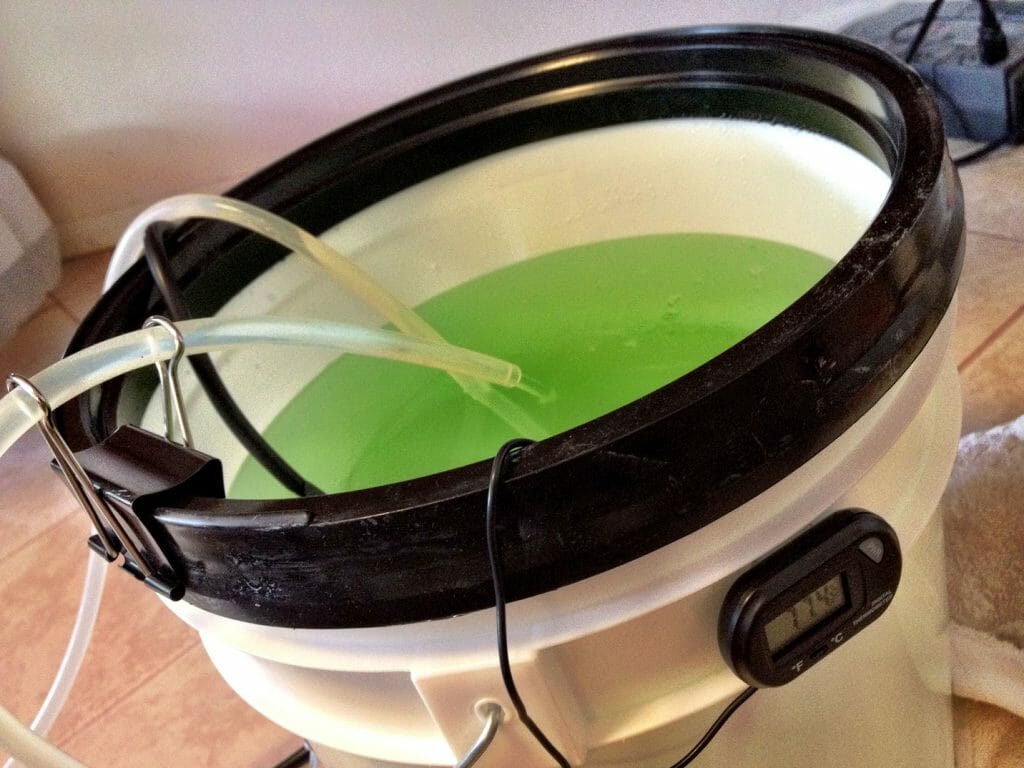
Cooling is provided by circulating distilled water through the tube with a pump. I set up a 5 gallon plastic bucket as the reservoir and, added an aquarium thermometer to monitor coolant temperature. This is required to avoid overheating and damaging the machine.
Another pump provides a modest “air assist,” which pushes smoke out of the way of the laser while cutting and, reduces deposition of vaporized particles on the lens.
A Little Focus
Part of the initial set up for the Blacktooth included aligning the mirrors. This requires a fairly high level of precision. I found some descriptions of various techniques in the forums and, with a couple hours of effort, I managed to get it all working. There are a few singed spots on the interior of the enclosure but, no serious complications.
In the Studio

I promptly built a low dolly out of plywood for the Blacktooth. This made it possible to push it under the main workbench in the studio when not in use.
Since the bottom of the Blacktooth is open, using the wood of the dolly as a backstop for cutting with the laser seemed like a bad idea. I covered the top of the dolly with large heavy ceramic tiles. While a 40-watt CO2 laser may be able to etch into the surface finish of the tile, it won’t be able to cut through it or heat it up enough to ignite the dolly.
I also purchased a steel “honeycomb” or “egg crate” tray. These make an excellent work surface. It reduces flashback (where the laser cuts through something and, reflects off of the surface behind it to damage the back of the stock being cut) and, makes it possible to use strong magnets to hold down lighter weight stock (like paper).

"Dots" Issue
I design and build a style of paper art pop up cards called origamic architecture. I had borrowed time on commercial laser cutters to produce some of my designs and, had always wanted my own laser for prototyping and production. So, I was very eager to get the Blacktooth working for that.

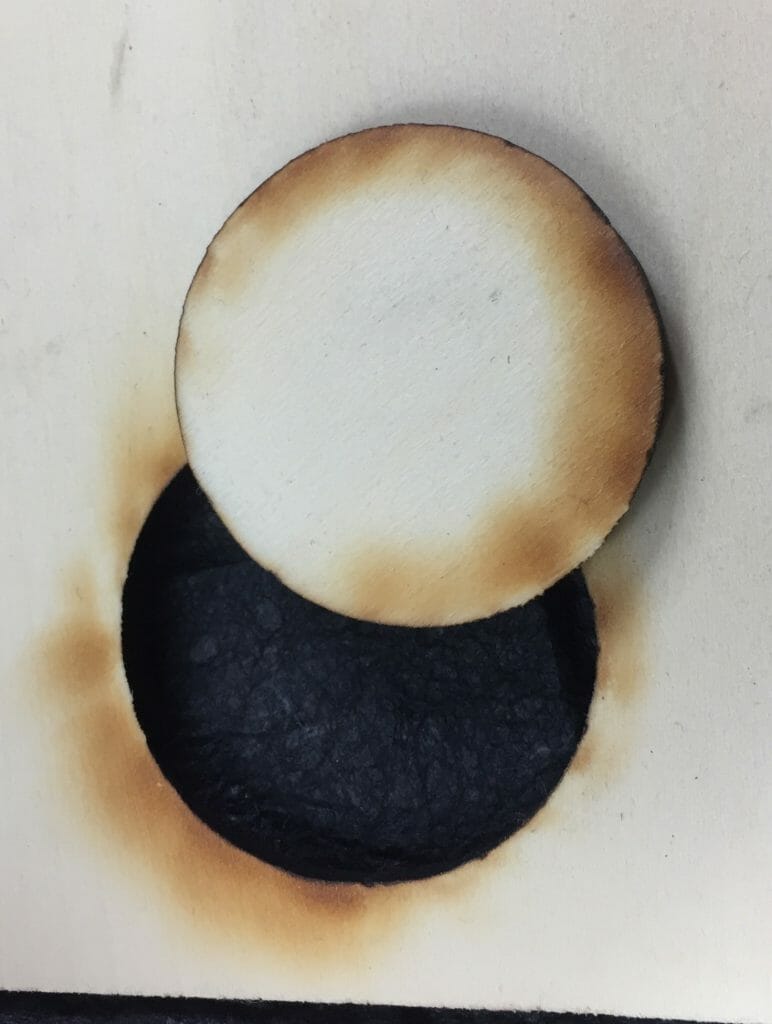
The gcode I was able to generate for the Blacktooth turned out to be unsuitable for cutting paper. For each vector cut, the laser would turn on. Then, the cutting head would move along the vector, stopping at the end. Then, the laser would turn off. This caused the laser to dwell at the start and end of each cut, producing a pronounced dot. While unlikely to be a serious problem on most heavier materials, this is completely unworkable for paper.
While I found other Blacktooth users who claimed to have resolved this issue, their CAM settings did not work for me. This is likely because their machines were significantly modified from the stock Blacktooth I was using.
It became clear to me that I would have to make some of these modifications to get the Blacktooth any closer to usable for my purposes.
Other Applications
 I did experiment briefly with cutting 1/8” hardwood ply with the Blacktooth. I cut a well-charred circle at something shy of full power with multiple passes. I also etched some lines into a piece of MDF. Now that I have a little more experience working with those on other machines, I can see where masking and a different approach would likely yield better results.
I did experiment briefly with cutting 1/8” hardwood ply with the Blacktooth. I cut a well-charred circle at something shy of full power with multiple passes. I also etched some lines into a piece of MDF. Now that I have a little more experience working with those on other machines, I can see where masking and a different approach would likely yield better results.
I never tried a raster engrave on the Blacktooth. I saw some other people’s experiments and, concluded that a DSP was really the best route to getting acceptable results.
DSP
By far the most popular upgrade for Blacktooth owners is a digital signal processor (DSP). In fact, later iterations of the Blacktooth from BuildYourCNC include a DSP.

I ordered the DSP most people seemed to be using (an AWC608). I checked with BuildYourCNC for some details on wiring it in and, got back some terse preliminary notes and, a promise that they would eventually have more detailed instructions.
While I do build and repair computers and have done some electronics work, rewiring idiosyncratic devices with high voltages and fragile, high-priced components is towards the edge of my comfort zone. So, my Blacktooth is currently sitting with its un-connected DSP gathering dust.
Other Upgrades
Reading what other users were posting the forums, it became clear that an upgrade to the air assist would likely also be in my future. Typically, people replace the basic pump used for the air assist with output from a small compressor (like those used for airbrush work).
I also aspired to filtering the output rather than just venting it out a window. This turns out to be non-trivial. Commercial solutions are very pricey and, assorted DIY projects that demonstrate any acceptable level of effectiveness are involved projects.
The Future
Now that I have a working Glowforge laser cutter, it seems even less likely that I will continue working on the Blacktooth. The Glowforge made the rapid transition to a usable tool that eluded me with the Blacktooth.
Now that I am using the Glowforge regularly for assorted projects, I see where the Blacktooth could be more useful, particularly with the DSP and air assist upgrades completed. The large cutting area is appealing.
The Blacktooth is an inexpensive laser cutter that would likely be a good fit for a small maker space where it can be adapted and maintained by people who like to tinker with their tools.
If you are within reasonable driving distance of Phoenix and, the Blacktooth sounds like a good fit for you or your organization, my slightly-used Blacktooth may be looking for a better home. Drop me a note.
With the Glowforge running $2495 for a Basic unit like mine, most people who don’t need the larger bed size and, are more interested in a working tool than a tool that is easy to customize, that is likely a better option. Note that you can get an even better price ($100 to $1500 better, depending on the model) by using my referral link [7].
Physical Dimensions
- Length and width: 37″ x 34″
- The height: 11.25″
- The weight: 70 lbs
Blacktooth Laser Cutter Costs
| Item | Required? | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Blacktooth Laser Cutter (shipped) | Y | $2200 |
| Cooling System | Y | $ 38 |
| Dolly | N | $ 115 |
| CamBam Plus software | N | $ 149 |
| MACH3 software | N | $ 159 |
| Laser Goggles | N | $ 82 |
| Steel Tray | N | $ 57 |
| DSP | N | $ 406 |
| Total | $3206 |